What is Tenses?
Tenses in English refer to the grammatical forms that indicate the time of an action, event, or state. There are three primary tenses in English: present, past, and future. Each tense can also have different forms to express continuous actions, completed actions, and ongoing actions at specific points in time. Here’s a brief explanation of each tense:
Present Tense:
- Simple Present: Used to describe actions, events, or states that are happening now or regularly occur. Example: “She reads books every day.”
- Present Continuous: Describes actions or events that are happening right now or are in progress. Example: “They are studying for their exams.”
- Present Perfect: Indicates actions or events that have just been completed or have relevance to the present moment. Example: “He has finished his homework.”
- Present Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that started in the past and are still ongoing or have recently stopped. Example: “She has been working here for five years.”
Past Tense:
- Simple Past: Used to talk about actions, events, or states that occurred and were completed in the past. Example: “They visited Paris last summer.”
- Past Continuous: Describes actions or events that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. Example: “He was reading a book when I called him.”
- Past Perfect: Indicates actions that were completed before another past action or a specific time in the past. Example: “She had already eaten dinner when we arrived.”
- Past Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that were ongoing for a period of time before another action or point in the past. Example: “They had been waiting for hours before the concert started.”
Future Tense:
- Simple Future: Used to talk about actions, events, or states that will happen in the future. Example: “She will arrive at 8 PM.”
- Future Continuous: Describes actions or events that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future. Example: “They will be celebrating their anniversary next week.”
- Future Perfect: Indicates actions that will be completed before a specified future time or action. Example: “He will have finished his project by Friday.”
- Future Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that will have been ongoing for a period of time before a specified future time. Example: “She will have been working here for ten years next month.”
Understanding tenses is crucial for expressing the timing of actions or events accurately in English sentences.
What are the three main types of tenses and why do we need them?
The three main types of tenses in English are present, past, and future. Each tense serves a specific purpose in indicating the timing of actions, events, or states. Here’s why we need these tenses:
Present Tense:
- Purpose: The present tense is used to describe actions, events, or states that are happening now, regularly occur, or have ongoing relevance to the present moment.
Structural formula:
Subject + verb (s/es) + object.
- Importance: It allows us to talk about current actions or habits (“She reads books every day”), ongoing events (“They are studying for their exams”), completed actions with present relevance (“He has finished his homework”), and continuous actions (“She has been working here for five years”).
Past Tense:
- Purpose: The past tense is used to talk about actions, events, or states that occurred and were completed in the past.
Structural formula:
Subject + verb (2nd form) + object.
- Importance: It helps us narrate past events (“They visited Paris last summer”), describe ongoing actions at a specific time in the past (“He was reading a book when I called him”), express actions completed before another past action (“She had already eaten dinner when we arrived”), and indicate ongoing actions in the past (“They had been waiting for hours before the concert started”).
Future Tense:
- Purpose: The future tense is used to discuss actions, events, or states that will happen in the future.
- Structural formula, Subject + shall/will+ verb (s/es) + object.
- Importance: It enables us to talk about future plans or predictions (“She will arrive at 8 PM”), ongoing actions at a specific time in the future (“They will be celebrating their anniversary next week”), actions completed before a future time or event (“He will have finished his project by Friday”), and ongoing actions leading up to a future time (“She will have been working here for ten years next month”).
We need these three main types of tenses in English to accurately express when actions occur, whether they are happening now, happened in the past, or will happen in the future. Tenses help us provide clarity, sequence events, and convey the temporal aspects of language.
What are the subtypes of tenses?
The subtypes of tenses in English are variations within the three main categories of present, past, and future tenses. These subtypes add nuance and specificity to the timing of actions, events, or states. Here are the subtypes of tenses:
Present Tense Subtypes:
- Simple Present: Describes actions, events, or states that are happening now or regularly occur. Example: “She reads books every day.”
- Present Continuous (Progressive): Describes actions or events that are happening right now or are in progress. Example: “They are studying for their exams.”
- Present Perfect: Indicates actions or events that have just been completed or have relevance to the present moment. Example: “He has finished his homework.”
- Present Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that started in the past and are still ongoing or have recently stopped. Example: “She has been working here for five years.”
Past Tense Subtypes:
- Simple Past: Used to talk about actions, events, or states that occurred and were completed in the past. Example: “They visited Paris last summer.”
- Past Continuous (Progressive): Describes actions or events that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. Example: “He was reading a book when I called him.”
- Past Perfect: Indicates actions that were completed before another past action or a specific time in the past. Example: “She had already eaten dinner when we arrived.”
- Past Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that were ongoing for a period of time before another action or point in the past. Example: “They had been waiting for hours before the concert started.”
Future Tense Subtypes:
- Simple Future: Used to talk about actions, events, or states that will happen in the future. Example: “She will arrive at 8 PM.”
- Future Continuous (Progressive): Describes actions or events that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future. Example: “They will be celebrating their anniversary next week.”
- Future Perfect: Indicates actions that will be completed before a specified future time or action. Example: “He will have finished his project by Friday.”
- Future Perfect Continuous: Expresses actions that will have been ongoing for a period of time before a specified future time. Example: “She will have been working here for ten years next month.”
These subtypes of tenses allow for a more precise and nuanced expression of time, helping speakers and writers convey the exact timing and duration of actions, events, or states in English.
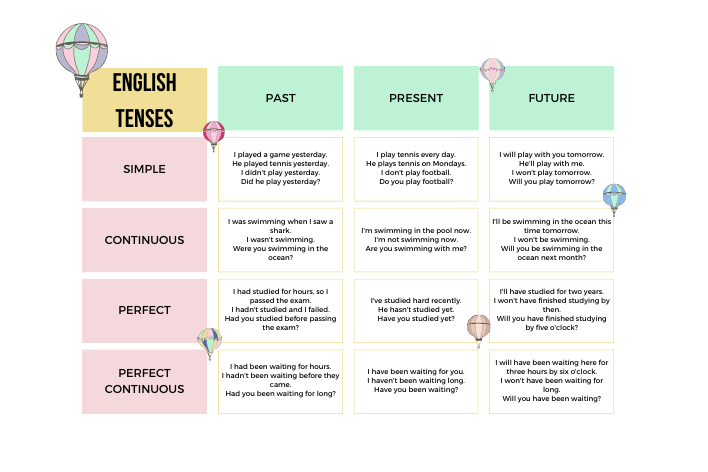
Example of Tenses in English
| Tense | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Simple Present | She reads books every day. |
| Present Continuous | They are studying for their exams. |
| Present Perfect | He has finished his homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | She has been working here for five years. |
| Simple Past | They visited Paris last summer. |
| Past Continuous | He was reading a book when I called him. |
| Past Perfect | She had already eaten dinner when we arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | They had been waiting for hours before the concert started. |
| Simple Future | She will arrive at 8 PM. |
| Future Continuous | They will be celebrating their anniversary next week. |
| Future Perfect | He will have finished his project by Friday. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | She will have been working here for ten years next month. |
50 examples of tenses in English, covering a range of present, past, and future tenses:
- Simple Present: She teaches English at the university.
- Present Continuous: They are studying for their exams.
- Present Perfect: He has finished his work already.
- Present Perfect Continuous: They have been working on this project for hours.
- Simple Past: She visited her parents last weekend.
- Past Continuous: He was reading a book when I called him.
- Past Perfect: She had already left when we arrived.
- Past Perfect Continuous: They had been waiting for hours before the show started.
- Simple Future: She will come to the party tomorrow.
- Future Continuous: They will be celebrating their anniversary next month.
- Future Perfect: He will have completed his assignment by then.
- Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been working here for five years next month.
- Simple Present: He always drinks coffee in the morning.
- Present Continuous: They are playing basketball right now.
- Present Perfect: She has visited that museum before.
- Present Perfect Continuous: They have been waiting for the bus since noon.
- Simple Past: I saw him at the mall yesterday.
- Past Continuous: She was cooking dinner when he arrived.
- Past Perfect: They had already finished eating when we got there.
- Past Perfect Continuous: He had been studying for hours before the exam.
- Simple Future: She will start her new job next week.
- Future Continuous: They will be traveling to Europe this summer.
- Future Perfect: He will have graduated by the end of the year.
- Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been living in the city for ten years by then.
- Simple Present: The train leaves at 7:00 AM every day.
- Present Continuous: He is working on a new project this week.
- Present Perfect: She has written three novels so far.
- Present Perfect Continuous: They have been renovating their house for months.
- Simple Past: He ran in the marathon last year.
- Past Continuous: They were dancing when the music stopped.
- Past Perfect: She had already left when I arrived at the party.
- Past Perfect Continuous: He had been waiting for hours before she called.
- Simple Future: She will arrive at the airport at 6:00 PM.
- Future Continuous: They will be working on the project next week.
- Future Perfect: He will have completed the course by then.
- Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been studying for hours by the time the exam starts.
- Simple Present: The sun rises in the east.
- Present Continuous: They are building a new house.
- Present Perfect: He has lived in this city for ten years.
- Present Perfect Continuous: She has been waiting for the bus since morning.
- Simple Past: She bought a new car last month.
- Past Continuous: They were watching a movie when the power went out.
- Past Perfect: He had already left when I arrived.
- Past Perfect Continuous: She had been working for hours before she took a break.
- Simple Future: They will arrive at the airport by 3:00 PM.
- Future Continuous: She will be cooking dinner when we get there.
- Future Perfect: He will have finished his homework before dinner.
- Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been studying for hours by the time the exam starts.
- Simple Present: The meeting starts at 9:00 AM sharp.
- Present Continuous: They are discussing the new project at the moment.
These examples showcase the use of different tenses in English to express actions, events, or states in various time frames.

